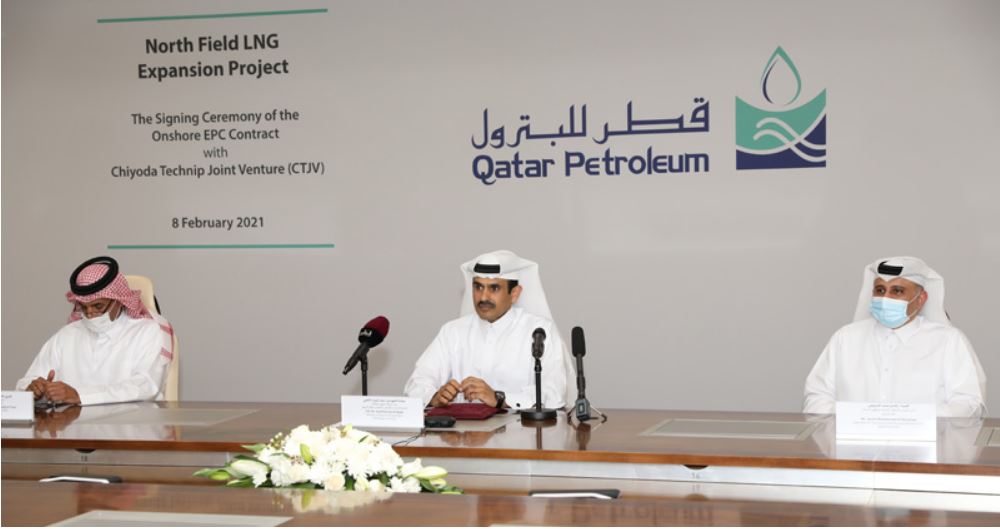
Qatar’s move to sanction the $30 billion North Field Expansion (NFE) project puts the country on course to return as the world’s largest liquefied natural gas (LNG) producer by 2030, a Rystad Energy report outlines, based on operational and so far sanctioned projects.
Qatar’s liquefaction capacity is forecast to rise to 110 million tonnes per annum (Mtpa), or 18 per cent of the global total, which is for now estimated at 600 Mtpa at the end of the decade.
Still, Rystad confirms that more projects are expected to be sanctioned as LNG demand will grow faster than supply.
Utilisation rates will not necessarily match the producers’ capacity in 2030. Rystad expects Qatar’s actual production in 2030 will reach 107 Mtpa, about 22.5 per cent of the so far global sanctioned supply of 476 Mtpa at the end of the decade – a great score with almost full capacity utilisation.
The U.S., on the other hand, is anticipated to likely produce 98 million tonnes of LNG by 2030, equivalent to a yearly utilisation rate of 91 per cent of its total capacity.
Australia is expected to see a significantly lower utilisation rate averaging 86 per cent of currently sanctioned capacity and produce about 76 million tonnes in 2030.
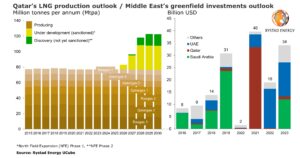
The NFE project is also making the Middle East the world’s top region for oil and gas project sanctioning in 2021.
Rystad expects rising oil prices will trigger sanctioning of global projects worth about $100 billion this year, of which the Middle East is set to contribute almost 40 per cent, or $40 billion.
More than 26 Middle Eastern projects worth a total of about $50 billion have been delayed over the past year, with NFE making up the lion’s share as it was pushed to 2021.
As this year got underway, the region had projects worth $98 billion due for sanctioning from 2021 to 2023.
With NFE now sanctioned, further investment commitments largely depend on developments in the UAE, where ADNOC aims to boost oil and gas production capacity and has a $40 billion project pipeline till 2025.
In Saudi Arabia, the oil price downcycle has hit ongoing bidding processes and Rystad estimates the giant Zuluf oil development worth $12 billion will be sanctioned in 2023.
Recovering prices are also likely to spur sanctioning activity in other parts of the region, especially in Oman, Iraq and Iran.
Among global LNG producers, Australia currently has the largest operating capacity of 88 Mtpa but is forecast to be surpassed by Qatar and the U.S. in the coming decade as new liquefaction capacity is commissioned.
The only Australian project expected to reach a final investment decision (FID) in 2021 is Woodside’s 4.5 Mtpa Pluto Train 2 project, which would be developed together with the Scarborough upstream asset.
The U.S. currently has 107 Mtpa of sanctioned LNG capacity, including 36 Mtpa under construction. Port Arthur LNG, Driftwood LNG, Plaquemines LNG and Freeport T4 have all signed long-term contracts or secured equity from LNG buyers, but will still need new deals to secure financing and move forward.
The proposed U.S. LNG projects have a breakeven price in the range of $6.5 to $7.5 per MMBtu delivered to Asia, compared to $4 per MMBtu for Qatar Petroleum’s North Field Expansion. While the Qatar Petroleum project has a lower breakeven price, U.S. LNG volumes have an advantage in the current large price differential between Henry Hub and Asian spot LNG prices.
Based on current sanctioning, Qatar is in the lead to be liquefaction capacity king in 2030, but there is a catch.
“According to Rystad Energy’s base case, global LNG demand will reach about 580 million tonnes by 2030, leaving significant room for bringing new LNG projects forward. We forecast that 104 Mtpa of new LNG supply must be sanctioned in the coming five years to meet the gap between actual supply and demand in 2030,” says Sindre Knutsson, vice president at Rystad Energy’s gas markets team.
To tap the supply capacity deficit, there are almost 1,000 Mtpa of new proposed capacity that will compete to attract buyers and investors to secure financing in the years ahead.
After a poor sanctioning year in 2020, Rystad believes that the optimism is back in the market and that more FIDs for LNG projects will follow after Qatar’s NFE.
Qatar, however, is also likely to add extra skin in the game, as it aims to increase its LNG output capacity to 126 Mtpa from the current 77 Mtpa through two expansion phases of the North Field.
The recently sanctioned first phase includes four new liquefaction trains to raise capacity to 110 Mtpa, while the second phase will include another two new trains currently in the front-end engineering design stage.
Rystad estimates the two phases will collectively reach the capacity targets by 2028 or 2029, if the second phase also gets the go-ahead.







